Architecture
Below is the architecture of OpenYurt.
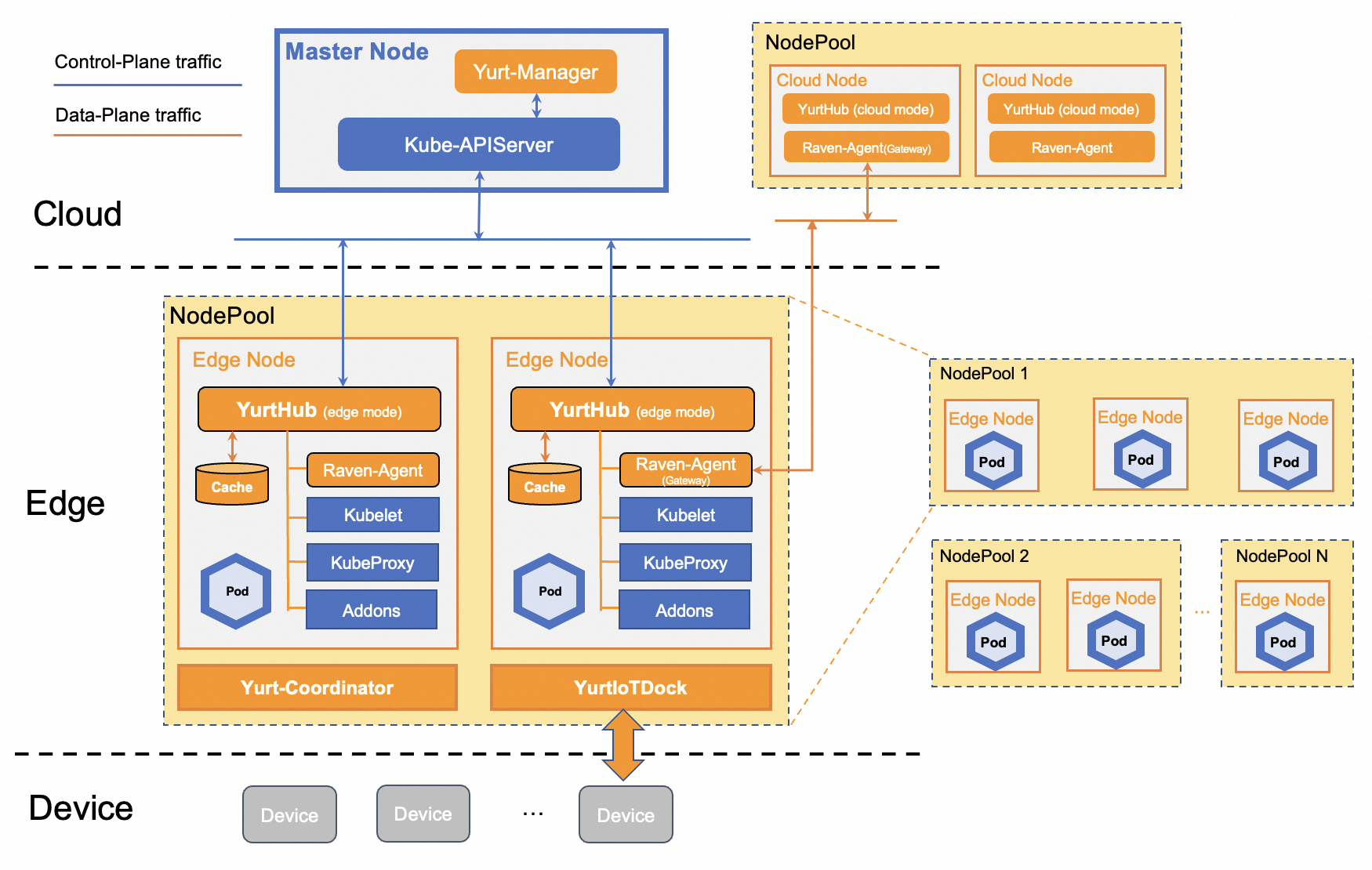
The blue box represents the original Kubernetes components, and the orange box represents the OpenYurt components.
Node category
- Cloud Node:The nodes running in cloud side, connecting to master with cloud intranet. Centralized control plane components are deployed in cloud side. The nodes are labeled with
openyurt.io/is-edge-worker: false. - Edge Node:The nodes running in edge side, connecting to master with public internet. They are usually close to edge production environment, and thus contains the mainly edge workloads. The nodes are labeled with
openyurt.io/is-edge-worker: true.
Traffic from edge to cloud kube-apiserver
YurtHub manages the network traffic from edge to cloud kube-apiserver and caches cloud data. Components in edge nodes such as kubelet, kube-proxy and flannel access the cloud kube-apiserver via YurtHub. When the edge nodes are disconnected from cloud, the caches are used to resume status to avoid workload disruption.
Traffic in data plane
Raven builds VPN channels to ensure connectivity from cloud to edge or edge to edge include the host network and the container network in order to achieve cloud to edge and edge to edge network communication, which is mainly due to the network domain of the edge node is not in the same network plane as the network domain on the cloud, and the edge nodes are not exposed on the public network.
OpenYurt Components
-
Raven-Agent:
- Raven is component of the OpenYurt to enhance cluster networking capabilities. This enhancement is focused on edge-edge and edge-cloud communication in OpenYurt. In short, it will provide layer 3 network connectivity among pods in different physical regions, as there are in one vanilla Kubernetes cluster.
- Deployment pattern: DaemonSet for Raven in all nodes.
-
YurtHub:
- YurtHub is a sidecar in node level, it performs the role of requests proxy between worker nodes and kube-apiserver. It has two running modes: edge and cloud. In edge mode, it caches data from the cloud and store it on the local disk. and the cached data is then utilized if connection between the cloud and edge network is lost, especially in scenarios where the node restarts after the interruption.
- Deployment pattern: Static pod in each node.
-
Yurt-Manager:
- The Yurt-Manager component consists of several controllers and webhooks, which are used to provide abilities to ensure that Kubernetes can work as it would in a normal data center in a cloud-edge collaboration scenario.
- Deployment pattern: The Yurt-Manager component is recommended to co-located with Kubernetes control plane components such as Kube-Controller-Manager. and Yurt-Manager is deployed as a
Deployment, usually consists of two instances, one leader and one backup.
-
YurtIoTDock:
- The former YurtDeviceController component has been integrated into the main repository of OpenYurt and no longer requires separate installation.
- OpenYurt enables seamless integration of EdgeX Foundry into cloud-native architecture for non-intrusive fusion in edge IoT solutions. This is achieved through cloud-native management of edge devices.
- Deployment Mode: Users can deploy YurtIoTDock on the edge side through the PlatformAdmin CR. Once YurtIoTDock is launched, it begins synchronizing edge device information to the corresponding Device, DeviceService, and DeviceProfile entities.
-
Yurt-Coordinator:
- Provide KV data storage (stored only in memory) and distributed lock capabilities in the node pool, so that YurtHub can elect a Leader, so as to realize heartbeat proxy, cloud edge traffic reuse, operation and maintenance monitoring in the node pool, etc.
- Deployment pattern: YurtAppDaemon and ensures one instance per edge node pool.